Product of Even Elements Haskell YouTube

This lesson provides a proper introduction to this surprisingly important data structure. You'll learn the basics of taking lists apart and putting them back together, as well as learning some of the essential functions for a list that Haskell provides. Finally, you'll take a peek at another unique feature of Haskell: lazy evaluation.
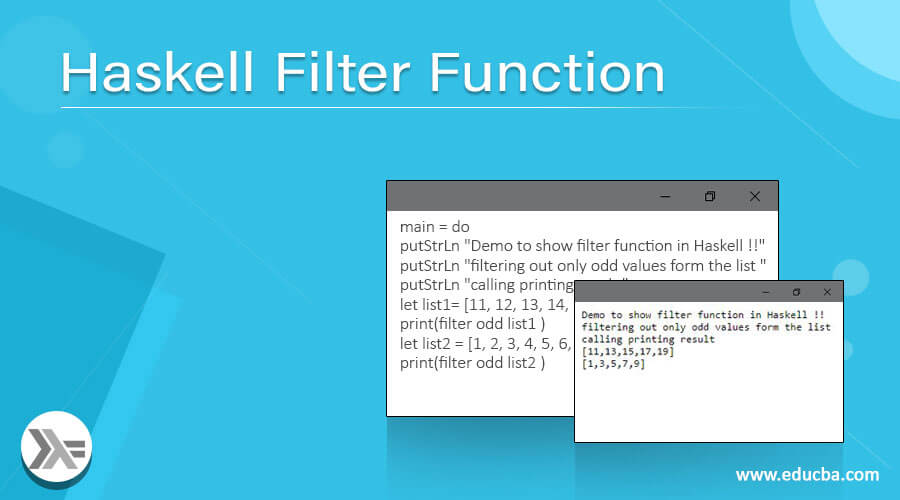
Haskell Filter Function How filter function works in Haskell?
indexList l = zip [1..(length l)] l. Mind you I'm not an Haskell expert, and there are probablly one million better ways to do it. 1. Reply. wizzup • 5 yr. ago. zip [1..] l would work too. If one input list is short, excess elements of the longer list are discarded. 6. Reply.
324, Haskell Sum every element in Matrix. YouTube

If you frequently access elements by index, it's probably better to use Data.Vector (from the vector package) or other data structures. Got any Haskell Language Question? Ask any Haskell Language Questions and Get Instant Answers from ChatGPT AI:
Haskell Programming Tutorial3 Comments and Local Function Definitions (English Version) YouTube
Finding a single element in a Haskell list. There are four commonly used ways to find a single element in a list, which vary slightly. find :: condition -> list -> Maybe element. The most general function for finding an element in a list that matches a given condition. Two things to note about this function:
Code Review Unique elements, long runtime Haskell YouTube

The basic idea is simple: We simply zip [0..] with the input list (ys) to get a list of tuples.The first element of each tuple is the index of the element in the list ys (input list). This allows us to perform index based tests in the helper function, as shown in insertHelper above.. Both left and right folds can be used for index based list operations.
PPT Haskell PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4145881

The function takes the element and returns Nothing if it is done producing the list or returns Just (a,b), in which case, a is a prepended to the list and b is used as the next element in a recursive call. For example, iterate f == unfoldr (\x -> Just (x, f x)) In some cases, unfoldr can undo a foldr operation:
Reading Characters From A String In Haskell A Comprehensive Guide

Haskell, therefore, does not treat arrays as general functions with an application operation, but as abstract data types with a subscript operation.. Finally, the index operation allows a particular element of an array to be addressed: given a bounds pair and an in-range index, the operation yields the zero-origin ordinal of the index within.
map function with previous and next list element in Haskell YouTube

They provide fast access to the first element in the list, and can quickly remove this element or add a new element as the "head" of the list. With all these features, lists work well as a "Stack" data structure - a Last-In-First-Out queue (LIFO). Depth-First-Search is an example of an algorithm where a basic list can get you started.
Haskell Programming Tutorial7 Type Basics revisited (English Version) YouTube

Function: findIndex. Type: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> Maybe Int. Description: Function find returns the first element of a list that satisfies a predicate, or Nothing, if there is no such element. findIndex returns the corresponding index. findIndices returns a list of all such indices. Related: elemIndex, elemIndices, find, findIndices. Example 1.
Haskell 4 Function syntax YouTube

Applied to a predicate and a list, any determines if any element of the list satisfies the predicate. For the result to be False, the list must be finite; True, however, results from a True value for the predicate applied to an element at a finite index of a finite or infinite list. all :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> Bool.
Making a parse error when learning about Index functions Learn Haskell Community

These functions mimic their counterparts in Data.List - imap, for instance, works like map but gives the index of the element to the modifying function. Note that left folds have the index argument after the accumulator argument - that's the convention adopted by containers and vector (but not lens). imap :: ( Int -> a -> b) -> [a] -> [b.
Haskell Programming Tutorial4Truth Values and Guards (English Version) YouTube
To get an element at a specific index in Haskell, you can use the '!!' operator. Think of this as selecting that stand-out piece from a catwalk collection. let a = [1,2,3,4,5,6] elementAtIndex = a !! 3. In this code snippet, we create a list, 'a', comprising six elements, and then use '!!' operator to retrieve the element at index 3.
Haskell Types YouTube
The function returns the next element of a list, following e. The first where binding is a function that splits the list, and puts the given element at the start, and wraps the rest to the end. I wouldn't say that it's circular, as it's only ever called once; the list it produces is still linear. The (x:[]) = Nothing line ensures that the list.
PPT CATCH Case and Termination Checker for Haskell PowerPoint Presentation ID6700219
Insert an element into the middle of a list. Generally, you will have to split the list into two smaller lists, put the new element to in the middle, and then join everything back together. For example: let (ys,zs) = splitAt n xs in ys ++ [new_element] ++ zs. Join two lists together. list1 ++ list2.
PPT Haskell PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1878191
1.3 Combining lists. 1.4 Accessing sublists. 1.5 Splitting lists. 2 Strings. 2.1 Multiline strings. 2.2 Converting between characters and values. 2.3 Reversing a string by words or characters. 2.4 Converting case. 2.5 Interpolation.
PPT Haskell PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4145881
I've just got into Haskell a few days ago and I love it. I'm looking for some pointers and best practices on how to organise and write Haskell code specifically when it comes to managing errors, which I have done using Maybe.. The following is an implementation of "select a list from a 2D list, take the last item from its nearest non empty left neighbour and put it at its head" which is going.